Diving into the world of variable interest rate loans, we uncover the dynamic nature of these financial instruments that can either be a boon or a bane for borrowers. Get ready for an enlightening journey through the realm of fluctuating interest rates and financial flexibility.
Let’s explore the ins and outs of variable interest rate loans, from understanding their definition to weighing the pros and cons against fixed-rate loans.
Definition of Variable Interest Rate Loans
Variable interest rate loans are loans where the interest rate can change over time based on fluctuations in the market. This is different from fixed-rate loans, where the interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan.
Examples of Financial Products
- Credit cards: Many credit cards have variable interest rates that can change based on the prime rate.
- Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs): ARMs have interest rates that adjust periodically based on market conditions.
- Student loans: Some student loans offer variable interest rates that can change with the market.
Benefits and Drawbacks
- Benefits:
- Lower initial interest rates: Variable rate loans often have lower initial rates compared to fixed-rate loans, which can result in lower initial monthly payments.
- Potential for lower rates: If interest rates decrease over time, borrowers with variable rate loans can benefit from lower overall interest costs.
- Drawbacks:
- Uncertainty: The main drawback of variable rate loans is the uncertainty of future interest rate changes, which can lead to higher monthly payments if rates rise.
- Risk of payment shock: Borrowers may experience payment shock if interest rates increase significantly, leading to higher monthly payments that they may not be able to afford.
Factors Influencing Variable Interest Rates
When it comes to variable interest rates, there are several key factors that can influence changes in these rates. Understanding these factors is crucial for borrowers who have variable rate loans as it can help them prepare for potential fluctuations in their interest payments.
Economic Indicators, Central Bank Policies, and Market Conditions are the main influencers of variable interest rates. Economic indicators such as inflation rates, GDP growth, and unemployment rates play a significant role in determining the direction of interest rates. Central bank policies, especially decisions on interest rates, can also have a direct impact on variable interest rates. Market conditions, including supply and demand for credit, can further contribute to rate changes.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide crucial information about the state of the economy, which in turn affects interest rates. For example, if inflation is high, central banks may increase interest rates to curb inflationary pressures. On the other hand, during periods of economic downturn, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth.
Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a pivotal role in setting short-term interest rates, which can influence variable interest rates. For instance, if a central bank decides to raise its benchmark interest rate, borrowers with variable rate loans may see an increase in their interest payments.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, such as the overall health of the financial markets and the demand for credit, can also impact variable interest rates. In times of economic uncertainty, lenders may tighten their lending criteria, leading to higher interest rates for borrowers.
Overall, borrowers can prepare for potential fluctuations in variable interest rates by staying informed about economic indicators, central bank policies, and market conditions. By monitoring these factors closely, borrowers can make informed decisions about their finances and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of interest rate changes.
Pros and Cons of Variable Interest Rate Loans
When it comes to variable interest rate loans, there are both advantages and risks that borrowers need to consider. Let’s dive into the pros and cons of opting for a variable interest rate loan.
Advantages of Variable Interest Rate Loans
Variable interest rate loans offer borrowers the potential to take advantage of lower interest rates in a falling rate environment. This means that if market interest rates decrease, borrowers could end up paying less in interest compared to fixed-rate loans. Additionally, variable interest rate loans often come with lower initial interest rates, making them an attractive option for those looking to save on interest costs initially.
Risks Associated with Variable Interest Rate Loans
On the flip side, the main risk associated with variable interest rate loans is the uncertainty of future interest rate movements. If market interest rates rise, borrowers could end up paying significantly more in interest compared to fixed-rate loans. This can lead to higher monthly payments and overall borrowing costs, potentially putting a strain on the borrower’s financial situation.
Strategies for Managing Risks Associated with Variable Interest Rate Loans
To mitigate the risks associated with variable interest rate loans, borrowers can consider a few strategies. One approach is to regularly monitor market interest rates and have a plan in place for potential rate increases. Another strategy is to make extra payments when rates are low to reduce the overall loan balance, which can help offset higher payments in the future. Refinancing to a fixed-rate loan when interest rates are favorable is also an option to consider for those looking for more stability in their loan payments.
Comparison with Fixed-Rate Loans
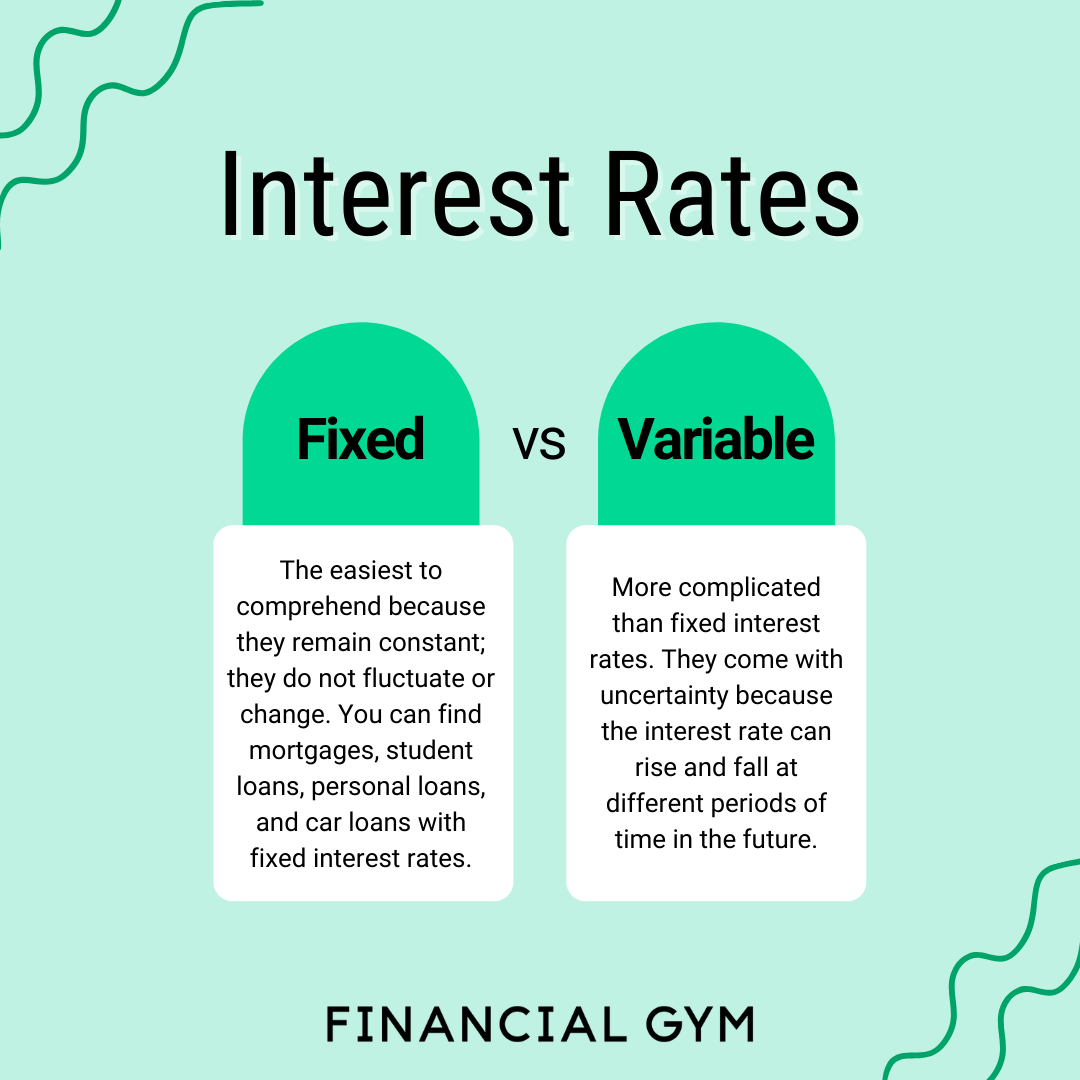
When comparing variable interest rate loans with fixed-rate loans, it’s essential to consider the stability and flexibility each option offers. While fixed-rate loans provide a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, variable interest rate loans can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Variable interest rate loans offer more flexibility in terms of potentially lower initial interest rates and the possibility of rates decreasing over time. This can result in lower overall interest payments compared to fixed-rate loans, especially if interest rates remain low or decrease.
Situations Favoring Variable Interest Rate Loans
- When economic conditions suggest that interest rates will remain low or decrease in the future.
- For short-term loans where the borrower plans to pay off the loan quickly before interest rates have a chance to increase significantly.
- When the borrower is comfortable with some level of risk and can handle potential fluctuations in monthly payments.
