Kicking off with Understanding wealth inequality, this topic delves into the complex dynamics of economic disparities that have plagued societies for centuries. From the evolution of wealth distribution to the impact of globalization, this overview will shed light on the various factors contributing to the unequal distribution of wealth.
As we explore historical events, economic factors, global perspectives, societal effects, and potential solutions, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the challenges posed by wealth inequality in today’s world.
Historical Overview of Wealth Inequality
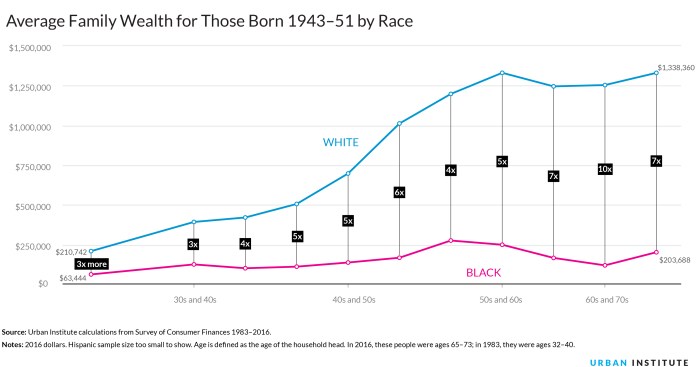
In understanding wealth inequality, it is crucial to examine its historical evolution to grasp the roots of the disparity that exists today. Over centuries, the distribution of wealth has undergone significant changes influenced by various factors such as economic policies, social structures, and technological advancements.
Feudal Systems and Monarchies
- The feudal systems of the Middle Ages concentrated wealth in the hands of monarchs, nobles, and clergy, creating vast disparities between the ruling class and the common people.
- Inheritance laws and primogeniture practices reinforced wealth concentration within noble families, limiting opportunities for upward mobility among the lower classes.
- The rise of mercantilism and colonialism further widened the wealth gap, as resources from colonies enriched the ruling powers at the expense of indigenous populations.
Industrial Revolution and Capitalism
- The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries ushered in a new era of wealth accumulation through industrialization and urbanization, leading to the emergence of wealthy industrialists and entrepreneurs.
- Innovations in technology and manufacturing enabled the creation of vast fortunes, while labor exploitation and poor working conditions contributed to the impoverishment of the working class.
- The laissez-faire economic policies of the time favored the accumulation of wealth by a few at the expense of the majority, exacerbating income inequality.
Modern Era and Globalization
- In the modern era, globalization has reshaped the distribution of wealth on a global scale, with multinational corporations and financial institutions wielding immense economic power.
- Neoliberal economic policies have promoted deregulation and privatization, leading to the concentration of wealth in the hands of a small elite while marginalizing vulnerable populations.
- The digital revolution and the rise of tech giants have created new sources of wealth, but have also widened the gap between the tech-savvy affluent and those left behind in the digital divide.
Factors Contributing to Wealth Inequality
In understanding wealth inequality, it is crucial to examine the various factors that contribute to the unequal distribution of wealth within a society.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping wealth distribution. This includes disparities in income levels, access to resources, and opportunities for economic advancement. The concentration of wealth in the hands of a few individuals or groups can further widen the wealth gap.
Education and Skill Levels
Education and skill levels are key determinants of an individual’s ability to accumulate wealth. Higher levels of education and specialized skills often lead to better job opportunities and higher income levels, which in turn can contribute to wealth accumulation over time.
Inheritance and Intergenerational Wealth Transfer
The role of inheritance and intergenerational wealth transfer cannot be overlooked when discussing wealth inequality. Inherited wealth can provide individuals with a significant financial advantage, allowing them to accumulate even more wealth over generations. This perpetuates a cycle of wealth concentration within certain families or social groups.
Global Perspectives on Wealth Inequality
In examining wealth distribution patterns across different countries, it is evident that disparities exist on a global scale. The impact of globalization has further exacerbated these inequalities, as wealth tends to concentrate in the hands of a few individuals or corporations. Various initiatives and policies have been proposed to address these global wealth disparities and promote a more equitable distribution of resources.
Wealth Distribution Patterns
- Many developed countries, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, have high levels of wealth inequality compared to developing nations.
- In countries like Sweden and Denmark, on the other hand, wealth is more evenly distributed among the population due to progressive taxation and social welfare programs.
- In emerging economies like China and India, rapid economic growth has led to an increase in wealth inequality, with a growing wealth gap between the rich and the poor.
Impact of Globalization
- Globalization has enabled multinational corporations to expand their operations worldwide, leading to the accumulation of wealth in the hands of a few global elites.
- Trade liberalization and outsourcing have also contributed to wealth disparities, as low-skilled workers in developing countries often face exploitation and low wages compared to their counterparts in developed nations.
- At the same time, globalization has created opportunities for economic growth and poverty reduction in some regions, but these benefits are not always equitably distributed among the population.
Initiatives to Address Wealth Disparities
- International organizations like the United Nations and the World Bank have called for policies that promote inclusive growth and reduce income inequality on a global scale.
- Some countries have implemented wealth taxes or inheritance taxes to redistribute wealth and reduce disparities between the rich and the poor.
- Social welfare programs, education reform, and job training initiatives are also critical in addressing wealth inequality and providing opportunities for socio-economic mobility.
Effects of Wealth Inequality on Society
In a society marked by wealth inequality, the impacts are far-reaching and affect various aspects of people’s lives.
Wealth Inequality and Social Mobility
The disparity in wealth distribution often hinders social mobility, making it harder for individuals from lower-income backgrounds to move up the economic ladder. Limited access to resources and opportunities can create barriers that impede upward mobility, perpetuating the cycle of poverty.
Wealth Disparities and Access to Healthcare and Education
Wealth inequality also influences access to essential services like healthcare and education. Individuals with greater wealth can afford better healthcare services and quality education, widening the gap in health outcomes and educational attainment between the affluent and the less affluent.
Psychological Effects of Living in a Society with High Wealth Inequality
The psychological impact of wealth inequality can be profound, leading to feelings of inadequacy, stress, and lower self-esteem among those who perceive themselves as being on the disadvantaged end of the wealth spectrum. This can contribute to social unrest and a sense of injustice within the society.
Solutions for Addressing Wealth Inequality
To tackle wealth inequality, policy measures need to be put in place to ensure a more equitable distribution of resources. Taxation plays a crucial role in redistributing wealth and promoting economic fairness. Alternative economic models can also be explored to achieve a more balanced wealth distribution.
Progressive Taxation
Progressive taxation involves taxing individuals with higher incomes at a higher rate than those with lower incomes. This approach not only generates revenue for government programs but also helps reduce the wealth gap by redistributing resources more evenly.
Universal Basic Income (UBI)
Universal Basic Income is a system where all citizens receive a regular, unconditional sum of money from the government. This ensures that everyone has a basic level of income to cover their needs, regardless of their socio-economic status. UBI can help alleviate poverty and reduce wealth inequality by providing a financial safety net for all individuals.
Investing in Education and Skills Training
By investing in education and skills training programs, individuals from lower-income backgrounds can acquire the necessary tools to increase their earning potential. This not only empowers individuals to improve their socio-economic status but also promotes a more equal distribution of wealth by enabling more people to access higher-paying jobs.
Corporate Regulation and Anti-monopoly Policies
Implementing regulations on corporations and enforcing anti-monopoly policies can help prevent the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few powerful entities. By promoting fair competition and preventing monopolistic practices, wealth can be distributed more evenly across society.
Community Wealth Building Initiatives
Community wealth building initiatives focus on empowering local communities to create and retain wealth within their neighborhoods. This approach involves supporting small businesses, cooperatives, and community-owned enterprises to ensure that wealth generated within a community stays within that community, benefiting its residents.
