Diving deep into the world of economic cycles, this introduction sets the stage for an intriguing exploration that will leave you feeling like you’re back in your high school days, but with a fresh and cool perspective.
Get ready to uncover the secrets behind economic cycles and how they shape the world around us.
Definition of Economic Cycles
Economic cycles refer to the fluctuations in economic activity that occur over time. These cycles are characterized by periods of expansion, peak, contraction, and trough.
Phases of Economic Cycles
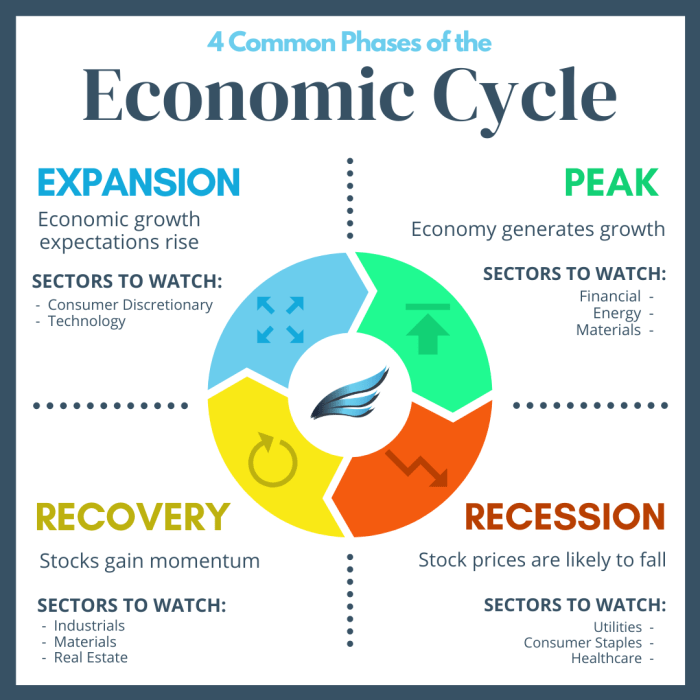
- The Expansion Phase: During this phase, the economy is growing, businesses are investing, and consumer spending is strong. Unemployment rates tend to decrease, and inflation may start to rise.
- The Peak Phase: This is the highest point of the economic cycle, where the economy is at its strongest. It is characterized by full employment, high consumer confidence, and increased production.
- The Contraction Phase: Also known as a recession, this phase sees a decline in economic activity. Businesses cut back on investments, consumer spending decreases, and unemployment rates rise.
- The Trough Phase: This is the lowest point of the economic cycle, where the economy is at its weakest. It is marked by high unemployment, low consumer confidence, and a decrease in production.
Examples of Historical Economic Cycles
- The Great Depression: The economic cycle of the 1930s, characterized by a severe contraction phase that lasted for several years, leading to high unemployment rates and widespread poverty.
- The Dot-Com Bubble: The economic cycle of the late 1990s and early 2000s, where excessive speculation in technology stocks led to a peak phase followed by a sharp contraction phase when the bubble burst.
- The Global Financial Crisis: The economic cycle of 2007-2009, triggered by the subprime mortgage crisis, resulted in a worldwide recession with a significant impact on financial markets and economies around the globe.
Factors Influencing Economic Cycles
Understanding the various factors that influence economic cycles is crucial for predicting and managing fluctuations in the economy.
Supply and Demand
Supply and demand play a significant role in shaping economic cycles. When demand for goods and services increases, it leads to an expansion phase in the economy. This increased demand can result in businesses ramping up production, creating more jobs, and boosting overall economic growth. Conversely, when demand decreases, it can lead to a contraction phase where businesses cut back on production, leading to job losses and a slowdown in economic activity.
Interest Rates
Interest rates have a direct impact on economic cycles. When central banks lower interest rates, it becomes cheaper for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This can stimulate spending and investment, leading to economic expansion. On the other hand, when interest rates are raised, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can slow down spending and investment, resulting in an economic contraction.
Government Policies
Government policies can also influence economic cycles. For example, expansionary fiscal policies such as increased government spending or tax cuts can stimulate economic growth during a downturn. Conversely, contractionary fiscal policies like austerity measures can help cool down an overheated economy and prevent inflation. Additionally, monetary policies implemented by central banks, such as quantitative easing or tightening, can also impact economic cycles by influencing the money supply and interest rates.
Indicators of Economic Cycles
In order to track economic cycles, analysts rely on key economic indicators that provide insights into the health of an economy. These indicators help in understanding the phase of the economic cycle and predicting future trends.
GDP Growth Rates
GDP growth rates play a crucial role in reflecting economic cycles. A rising GDP growth rate indicates a growing economy, typically associated with an expansionary phase of the economic cycle. Conversely, a declining GDP growth rate may signal an economic slowdown or contraction. It is important to monitor GDP growth rates to gauge the overall health of the economy and anticipate potential shifts in the economic cycle.
- High GDP growth rates: Indicates a period of economic expansion, characterized by increased consumer spending, business investments, and overall economic activity.
- Low or negative GDP growth rates: Suggests an economic contraction, with reduced consumer confidence, lower business investments, and potential job losses.
Unemployment Rates
Unemployment rates are another critical indicator when it comes to understanding economic cycles. High unemployment rates often coincide with economic downturns, reflecting reduced job opportunities and weaker consumer spending. On the other hand, low unemployment rates signify a healthy economy with more job opportunities and higher consumer confidence.
Monitoring changes in unemployment rates can provide valuable insights into the phase of the economic cycle and help policymakers make informed decisions to stabilize the economy.
Effects of Economic Cycles
When it comes to economic cycles, businesses, consumer behavior, and investments are all impacted in various ways.
Businesses
- During a recession, businesses may experience a decrease in demand for their products or services, leading to lower revenues and potential layoffs.
- Conversely, during an expansion phase, businesses may see an increase in demand, allowing them to expand operations and hire more employees.
- Overall, economic cycles can greatly affect the profitability and sustainability of businesses.
Consumer Behavior
- During a recession, consumers tend to cut back on spending, especially on non-essential items, in an effort to save money and weather the economic downturn.
- On the flip side, during an expansion phase, consumers may feel more confident in their financial situation and be more willing to spend on luxury goods or experiences.
- Economic cycles play a significant role in shaping consumer habits and purchasing decisions.
Investments
- Investors often adjust their investment strategies based on where the economy is in the cycle. For example, during a recession, they may focus on safer investments like bonds or dividend-paying stocks.
- During an expansion phase, investors may take on more risk and invest in growth stocks or commodities to capitalize on the upward trend in the economy.
- The performance of investments can be heavily influenced by economic cycles, making it crucial for investors to stay informed and adapt their strategies accordingly.
