Hey there, all you cool cats and kittens! Today, we’re diving deep into the world of retirement account contributions. Buckle up and get ready to learn about the ins and outs of securing your financial future with some savvy money moves.
From understanding the importance of contributions to exploring different account types and strategies for maximizing your savings, this guide has got you covered. So, grab a snack and let’s get this financial party started!
Importance of Retirement Account Contributions
Contributing to retirement accounts is essential for securing financial stability during the post-working years. By consistently setting aside a portion of income, individuals can build a nest egg that will support them in retirement. This proactive approach to saving ensures that individuals can maintain their desired lifestyle without relying solely on social security benefits or other sources of income.
Long-Term Benefits of Regular Contributions
Regular contributions to retirement accounts have the potential to grow significantly over time due to the power of compound interest. As contributions are invested and earn returns, the account balance can snowball, resulting in substantial growth. This growth can provide a comfortable cushion for retirement and allow individuals to enjoy their golden years without financial stress.
Starting Early vs. Starting Later in Life
Starting early with retirement account contributions yields greater benefits due to the longer time horizon for investments to grow. Even small contributions made in one’s 20s or 30s can accumulate substantial wealth by the time retirement age is reached. On the other hand, starting later in life requires larger contributions to catch up, which may be more challenging to achieve.
Examples of Growth Over Time
For example, if an individual starts contributing $200 per month to a retirement account at age 25 and earns an average annual return of 7%, they could potentially have over $600,000 saved by age 65. In contrast, if another individual starts contributing the same amount at age 40, they would only have around $200,000 saved by age 65, assuming the same rate of return. This demonstrates the significant impact of starting early on retirement savings.
Types of Retirement Accounts
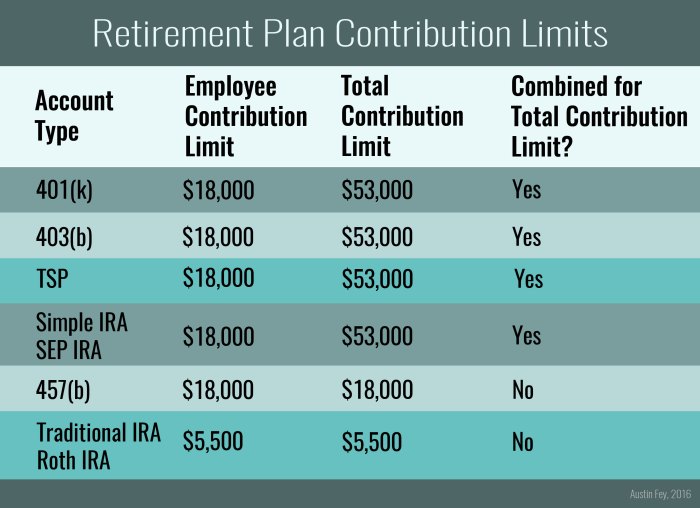
When it comes to saving for retirement, there are different types of retirement accounts you can choose from. Each type has its own set of rules, benefits, and eligibility criteria. Let’s break it down for you.
401(k) Retirement Account
- 401(k) accounts are employer-sponsored retirement plans that allow employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income towards retirement.
- Eligibility: Typically, employees of companies that offer 401(k) plans are eligible to participate.
- Tax Implications: Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income for the year.
- Contribution Limits: For 2021, the annual contribution limit for 401(k) accounts is $19,500, with an additional catch-up contribution of $6,500 for those aged 50 and older.
Traditional IRA
- A Traditional IRA is an individual retirement account that allows individuals to contribute pre-tax dollars towards retirement.
- Eligibility: Anyone under the age of 70 ½ with earned income can contribute to a Traditional IRA.
- Tax Implications: Contributions are tax-deductible, and your investments grow tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement.
- Contribution Limits: For 2021, the annual contribution limit for Traditional IRAs is $6,000, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 for those aged 50 and older.
Roth IRA
- A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account that allows individuals to contribute after-tax dollars towards retirement.
- Eligibility: There are income limits for Roth IRA contributions, and individuals must meet certain criteria to be eligible.
- Tax Implications: Contributions to a Roth IRA are not tax-deductible, but qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
- Contribution Limits: For 2021, the annual contribution limit for Roth IRAs is $6,000, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 for those aged 50 and older.
Strategies for Maximizing Retirement Contributions
When it comes to securing a comfortable retirement, maximizing contributions to your retirement accounts is crucial. By following specific strategies, you can boost your savings and set yourself up for a financially stable future.
Employer Matching Contributions
Employer matching contributions are essentially free money that your employer adds to your retirement savings based on a percentage of your own contributions. Take full advantage of this benefit by contributing at least enough to meet the employer match. For example, if your employer matches 50% of your contributions up to 6% of your salary, make sure you contribute at least 6% to get the full match.
Catch-Up Contributions
For individuals nearing retirement age, catch-up contributions are a valuable tool to accelerate savings. Once you reach the age of 50, you are eligible to make additional contributions to your retirement accounts beyond the standard limits. For example, in 2021, individuals aged 50 and older can make an extra $6,500 catch-up contribution to their 401(k) on top of the $19,500 standard limit.
Budgeting Techniques
Implementing effective budgeting techniques can help you increase your retirement savings over time. Start by creating a detailed budget that Artikels your income, expenses, and savings goals. Identify areas where you can cut back on spending and allocate those savings towards your retirement accounts. Consider automating your contributions to ensure consistency and discipline in saving for retirement.
Impact of Retirement Account Contributions on Taxes
When it comes to saving for retirement, considering the impact of your contributions on taxes is crucial. By understanding how retirement account contributions can affect your tax liabilities, you can make informed decisions to maximize your savings.
Tax Advantages of Contributing to Retirement Accounts
- Contributions to traditional retirement accounts, such as a 401(k) or traditional IRA, are typically tax-deductible. This means that the amount you contribute is deducted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of income subject to taxation.
- For Roth retirement accounts, like a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k), contributions are made with after-tax dollars. While you don’t get an immediate tax deduction, qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, providing tax-free growth on your investments.
Differences in Tax Treatment for Traditional and Roth Retirement Accounts
- In traditional retirement accounts, contributions are tax-deductible, but withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- On the other hand, Roth retirement accounts offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement, as long as certain conditions are met, making them a valuable tax planning tool.
How Retirement Contributions Can Lower Taxable Income
- For example, if you contribute $5,000 to a traditional 401(k) in a year where your taxable income is $50,000, your taxable income would be reduced to $45,000. This means you would pay taxes on $5,000 less income, potentially lowering your tax bill.
- By strategically contributing to retirement accounts, you can not only save for the future but also enjoy tax benefits that can help reduce your current tax burden.
