Diving into the world of inflation hedging, get ready to explore the ins and outs of this financial strategy that keeps investors on their toes. From gold to real estate, we’re about to break down the key players in this game of financial protection.
As we uncover the different assets and strategies used to combat the impact of inflation, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how to safeguard your investments in a dynamic market.
Definition of Inflation Hedging
Inflation hedging is a strategy used by investors to protect the real value of their assets against the erosion caused by inflation. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, making it crucial for investors to find ways to mitigate this risk.
Assets for Inflation Hedging
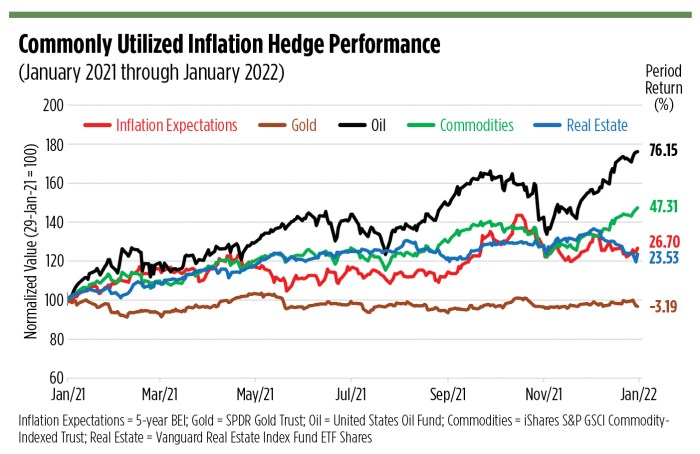
- Real Estate: Investment in properties can act as a hedge against inflation as property values tend to increase over time.
- Commodities: Investing in commodities like gold, silver, or oil can provide a hedge against inflation as their prices often rise in inflationary environments.
- TIPS (Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities): These securities are specifically designed to protect against inflation by adjusting their principal value based on changes in the Consumer Price Index.
Importance of Inflation Hedging in Investment Portfolios
Inflation hedging is important in investment portfolios as it helps maintain the purchasing power of the portfolio over the long term. By including assets that have the potential to outpace inflation, investors can ensure that their wealth retains its value and continues to grow even in inflationary environments.
Gold as an Inflation Hedge
Gold has long been considered a traditional inflation hedge due to its unique properties and historical performance.
Comparing Gold to Other Assets
- Gold is often compared to other assets like stocks and bonds in terms of its effectiveness as an inflation hedge.
- Unlike paper currencies, gold maintains its intrinsic value over time and tends to hold its purchasing power during periods of high inflation.
- Gold is a tangible asset that is not tied to any government or central bank, making it a popular choice for investors seeking protection against inflation.
Historical Data Supporting Gold’s Role
- Historical data shows that gold has consistently outperformed other assets during times of high inflation.
- During periods of economic uncertainty or inflationary pressures, gold prices tend to rise as investors flock to safe-haven assets.
- For example, during the 1970s when inflation in the United States surged, the price of gold skyrocketed, outpacing the returns of stocks and bonds.
Real Estate as an Inflation Hedge
Real estate is often considered a reliable hedge against inflation due to its ability to maintain or increase in value over time, keeping pace with rising prices in the economy. This can help investors preserve the real value of their assets and generate returns that outpace inflation.
Pros and Cons of Using Real Estate for Inflation Hedging
- Pros:
- Appreciation: Real estate values tend to increase over time, providing a natural hedge against inflation.
- Rental Income: Rental properties can generate consistent income streams that may also rise with inflation.
- Tax Benefits: Real estate investors can take advantage of tax deductions and benefits that can help offset inflationary pressures.
- Cons:
- Liquidity Risk: Real estate investments are not as liquid as other assets, making it challenging to quickly access funds in times of need.
- Maintenance Costs: Property upkeep and maintenance expenses can eat into returns, affecting the overall effectiveness of the hedge.
- Market Volatility: Real estate markets can experience fluctuations, impacting the value of the investment and its ability to hedge against inflation.
Real Estate Investment Strategies to Mitigate Inflation Risks
- Diversification: Investing in a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial properties can help spread risk and maximize returns.
- Long-Term Leases: Securing long-term leases with rental properties can provide stable income streams that are less sensitive to short-term inflationary pressures.
- Property Improvements: Making strategic renovations or upgrades to real estate assets can increase their value and better position them against inflation.
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
TIPS, or Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, are bonds issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury specifically designed to provide protection against inflation. Unlike traditional bonds, the principal value of TIPS adjusts based on changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures inflation.
How TIPS Work as an Inflation Hedge
TIPS offer investors a way to safeguard their investment against inflation by adjusting the principal value in line with the CPI. This means that as inflation rises, the value of TIPS increases, thus providing a real return that keeps pace with inflation.
Comparing TIPS to Other Fixed-Income Securities
- TIPS provide a higher level of inflation protection compared to traditional fixed-income securities like regular Treasury bonds or corporate bonds.
- While traditional bonds pay a fixed interest rate, the interest payments on TIPS adjust based on the inflation-adjusted principal value, providing better protection against rising prices.
- Investors holding TIPS can be assured that their investment will preserve its real value over time, making them a preferred choice for inflation hedging.
Risks Associated with Investing in TIPS for Inflation Hedging
- Interest Rate Risk: TIPS are sensitive to changes in interest rates, and fluctuations in rates can impact the market value of TIPS.
- Deflation Risk: In periods of deflation, TIPS may underperform compared to traditional bonds as the inflation adjustment feature works in reverse.
- Liquidity Risk: TIPS may not be as liquid as other fixed-income securities, especially in times of market stress, which can affect the ability to buy or sell them at favorable prices.
