Diving deep into the realm of high-interest credit cards, this introduction sets the stage for an intriguing exploration that will captivate readers with its unique insights and information. Get ready to uncover the secrets of high-interest credit cards in a way that’s both informative and engaging.
In the following paragraphs, we’ll break down the key aspects of high-interest credit cards, shedding light on their impact, risks, and benefits in the financial world.
Overview of High-Interest Credit Cards
High-interest credit cards are a type of credit card that come with significantly higher interest rates compared to regular credit cards. These cards are usually offered to individuals with lower credit scores or limited credit history.
Typical Interest Rates
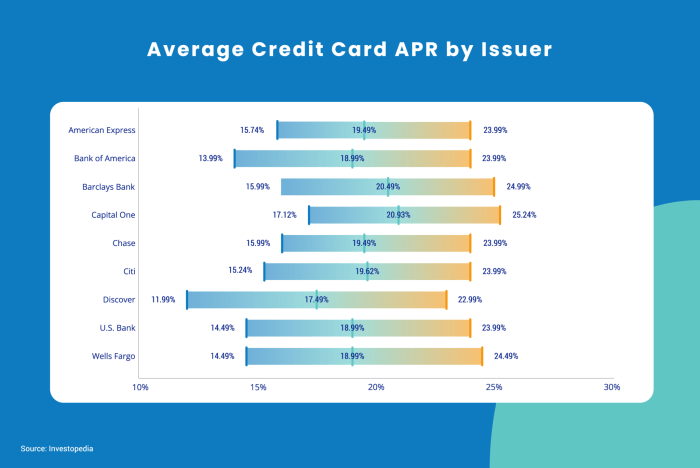
High-interest credit cards typically come with interest rates ranging from 20% to 25% or even higher. This means that if you carry a balance on your card, you could end up paying a substantial amount in interest charges over time.
Risks and Benefits
- Risks: Using a high-interest credit card can lead to mounting debt if you are unable to pay off your balance in full each month. The high interest rates can quickly escalate the amount you owe, making it challenging to get out of debt.
- Benefits: On the flip side, high-interest credit cards can be a good option for individuals looking to build or improve their credit score. By using the card responsibly and making timely payments, you can demonstrate creditworthiness to lenders.
Factors Contributing to High-Interest Rates
When it comes to high-interest rates on credit cards, there are several key factors at play that contribute to the rates that customers are charged. Credit card companies take into account various elements when determining the interest rates for individual customers. Additionally, economic conditions play a significant role in influencing the interest rates that credit card companies offer.
Credit Score
Credit card companies often base their interest rate decisions on the credit score of the individual applying for the card. A higher credit score typically results in a lower interest rate, as it indicates a lower risk for the credit card company. On the other hand, individuals with lower credit scores may be charged higher interest rates to offset the increased risk.
Market Conditions
The overall economic conditions and market trends can impact the interest rates on credit cards. When interest rates set by the Federal Reserve are high, credit card companies may also increase their rates to maintain profitability. Conversely, during times of economic downturn or low interest rates, credit card companies may offer lower rates to attract more customers.
Payment History
Another factor that contributes to high-interest rates is the payment history of the cardholder. Individuals who consistently make late payments or only pay the minimum amount due may be considered higher risk by credit card companies. As a result, these individuals may face higher interest rates as a way for the company to mitigate potential losses.
Credit Utilization Ratio
The credit utilization ratio, which is the amount of credit being used compared to the total available credit, also plays a role in determining interest rates. High credit utilization can signal financial distress and may lead to higher interest rates on credit cards. On the other hand, individuals with low credit utilization ratios may be offered more favorable interest rates.
Impact of High-Interest Credit Cards on Consumers
High-interest credit cards can have a significant impact on consumers’ financial well-being. When individuals carry balances on these cards, they often end up paying a substantial amount of money in interest fees, which can lead to financial strain and debt accumulation.
Financial Effects of High-Interest Credit Cards
- Consumers may find themselves struggling to make minimum payments, leading to a cycle of debt that is difficult to break.
- Accruing high-interest charges can result in paying much more for purchases over time than the original cost.
- Credit card debt can negatively impact credit scores, making it harder to secure loans or obtain favorable interest rates in the future.
Strategies for Managing High-Interest Credit Card Debt
- Creating a budget and cutting unnecessary expenses to allocate more money towards paying off credit card balances.
- Consolidating debt through balance transfers to lower-interest cards or seeking a personal loan with a lower interest rate.
- Communicating with creditors to negotiate lower interest rates or develop a repayment plan that fits within the consumer’s budget.
Long-Term Consequences of Carrying Balances on High-Interest Credit Cards
- Continuously carrying high balances can lead to a cycle of debt that becomes increasingly difficult to escape.
- High levels of credit card debt can hinder long-term financial goals, such as saving for retirement or purchasing a home.
- Defaulting on credit card payments can result in legal action, wage garnishment, and a damaged credit history that persists for years.
Comparison with Low-Interest Credit Cards
When comparing high-interest credit cards with low-interest credit cards, it’s essential to consider the interest rates charged on balances carried over from month to month. Low-interest credit cards typically have lower APRs, while high-interest credit cards come with significantly higher interest rates.
Advantages of High-Interest Credit Cards
- High-interest credit cards may be more advantageous in situations where individuals plan to pay off their balance in full each month. Since the interest rate won’t come into play if the balance is cleared monthly, individuals can benefit from other features and rewards offered by these cards.
- For individuals with a good credit score and a solid financial plan in place, high-interest credit cards can provide access to lucrative rewards programs, cashback offers, and travel benefits that may outweigh the impact of the high-interest rates.
- High-interest credit cards can also serve as a tool for building credit history and improving credit scores if used responsibly, even if the interest rates are higher than those of low-interest credit cards.
Features of Low-Interest Credit Cards
- Low-interest credit cards typically offer lower APRs, making them ideal for individuals who anticipate carrying a balance on their cards from month to month. This can result in significant savings on interest payments over time.
- Some low-interest credit cards come with introductory 0% APR offers on purchases and balance transfers, allowing cardholders to save on interest charges for a specified period.
- Low-interest credit cards may have fewer fees associated with them, such as annual fees or balance transfer fees, making them a cost-effective option for individuals looking to manage their finances efficiently.
