Yo, we diving into the world of growth vs value stocks. Buckle up as we break down the differences and similarities between these two investment strategies that can make or break your portfolio.
Growth vs Value Stocks
Growth stocks are shares in companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies in the market. On the other hand, value stocks are undervalued by the market and are considered to be trading at a lower price relative to their fundamentals.
The key differences between growth and value stocks lie in their investment strategies. Growth stocks typically reinvest their earnings back into the company for further growth, while value stocks are often seen as bargain buys with the potential for price appreciation.
Examples of Growth Stocks
- Amazon (AMZN) – Known for its continuous innovation and expansion into new markets.
- Netflix (NFLX) – A disruptor in the entertainment industry with a focus on streaming services.
Examples of Value Stocks
- Walmart (WMT) – A retail giant with a strong presence and steady cash flow.
- Exxon Mobil (XOM) – An energy company with stable revenues and dividend payouts.
Factors Influencing Growth Stocks
When it comes to growth stocks, there are several key factors that can influence their classification and performance in the market. These factors play a crucial role in determining whether a stock is considered a growth stock or not. Let’s delve into some of the main factors that impact growth stocks.
Identifying Growth Stocks
- Growth Potential: One of the primary factors that make a stock classify as a growth stock is its potential for rapid and substantial growth in earnings and revenue.
- High Price/Earnings Ratio: Growth stocks typically have a higher P/E ratio compared to value stocks, reflecting the market’s confidence in their future growth prospects.
- Strong Market Presence: Companies with a strong market presence, disruptive business models, and innovative products or services are often classified as growth stocks.
Impact of Economic Conditions
Economic conditions can significantly impact growth stocks, as they are more sensitive to changes in the market environment. During periods of economic expansion, growth stocks tend to outperform value stocks due to their growth potential. However, during economic downturns, growth stocks may face challenges as investors become more risk-averse.
Role of Innovation and Technology
Innovation and technology play a critical role in driving growth stocks. Companies that are at the forefront of technological advancements and innovation are more likely to be classified as growth stocks. These companies have the potential to disrupt traditional industries, create new markets, and drive substantial growth in earnings and revenue.
Factors Influencing Value Stocks
Value stocks are characterized by being undervalued by the market in relation to their intrinsic value. Several factors influence whether a stock is classified as a value stock, how market trends can impact these stocks, and the role financial metrics play in evaluating them.
Identifying Value Stocks
- Low Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio: Value stocks typically have a lower P/E ratio compared to growth stocks. This indicates that the stock is cheaper relative to its earnings.
- High Dividend Yield: Value stocks often offer higher dividend yields, making them attractive to income-seeking investors.
- Low Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio: A low P/B ratio suggests that the stock is trading below its intrinsic value, making it a potential value investment.
Market Trends Impact
- Market Cycles: Value stocks tend to perform well during periods of economic uncertainty or market downturns, as investors seek out stable and undervalued assets.
- Sector Rotation: Changes in market sentiment can lead to shifts in investor preferences between growth and value stocks, impacting the performance of value stocks.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can affect the attractiveness of value stocks, as higher rates may make dividend-paying value stocks more appealing.
Financial Metrics in Evaluation
- Price-to-Earnings Growth (PEG) ratio: The PEG ratio combines the P/E ratio with the expected earnings growth rate of a company, providing a more comprehensive view of the stock’s valuation.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: A low debt-to-equity ratio is often favorable for value stocks, as it indicates financial stability and lower risk.
- Free Cash Flow: Examining a company’s free cash flow can help determine its ability to generate cash and fund operations, a key consideration for value investors.
Performance Comparison
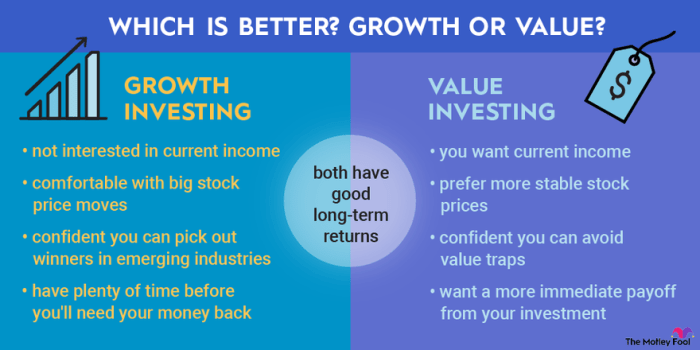
When comparing the historical performance of growth stocks versus value stocks, it is essential to consider the long-term trends and market conditions that influence their returns.
Historical Performance
Overall, growth stocks have outperformed value stocks in recent years, especially during periods of economic expansion and bull markets. Growth stocks typically represent companies with high growth potential and innovative technologies, leading to higher returns for investors. On the other hand, value stocks, which are considered undervalued by the market, tend to perform better during economic downturns and bear markets.
Market Conditions
During periods of economic growth and low interest rates, growth stocks tend to shine due to their potential for high earnings growth. However, when market conditions shift towards uncertainty or recession, value stocks may offer more stability and resilience. It is crucial for investors to diversify their portfolios to mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations.
Long-Term Investment
For long-term investment strategies, a balanced approach that includes both growth and value stocks may be more suitable. While growth stocks offer the potential for significant returns, value stocks provide stability and income generation. By combining both types of stocks in a portfolio, investors can benefit from diversification and capitalize on opportunities in different market conditions.
