Get ready to dive into the world of financial planning for retirement. We’re about to break down the ins and outs of preparing for your golden years, so buckle up and let’s get started.
Whether you’re a high school student dreaming of early retirement or a seasoned professional looking to fine-tune your financial strategy, this guide has got you covered.
Introduction to Financial Planning for Retirement
Financial planning for retirement involves creating a strategy to help you achieve your financial goals during your retirement years. This includes saving, investing, and managing your money wisely to ensure a comfortable retirement.
It is crucial to start early with retirement planning to take advantage of compounding interest and maximize your savings. The earlier you start saving for retirement, the more time your money has to grow and the less you will have to save each month to reach your goals.
Key Factors to Consider in Retirement Financial Planning
- Income Needs: Calculate how much income you will need in retirement to maintain your desired lifestyle. Consider expenses such as housing, healthcare, and leisure activities.
- Retirement Age: Determine at what age you plan to retire and how many years of retirement you need to plan for. This will impact how much you need to save.
- Investment Strategy: Develop an investment strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance, goals, and timeline. Consider diversifying your investments to manage risk.
- Social Security and Pension: Factor in any expected income from Social Security or pension plans into your retirement planning. Understand how these benefits will contribute to your overall income.
- Healthcare Costs: Plan for healthcare expenses in retirement, including insurance premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs. Consider long-term care needs as well.
Setting Retirement Goals
Setting specific retirement goals is crucial in creating a roadmap for your financial future. By defining your goals, you can tailor your financial planning strategies to ensure you have enough savings to support the lifestyle you desire during retirement.
When setting retirement goals, it is important to consider both short-term and long-term objectives. Short-term goals may include saving a certain amount of money each month, paying off debt, or building an emergency fund. Long-term goals, on the other hand, could involve determining the age at which you want to retire, estimating your desired retirement income, or planning for major expenses like healthcare or travel.
Examples of Short-term and Long-term Retirement Goals
- Short-term goal: Save $500 per month in a retirement account
- Short-term goal: Pay off all credit card debt within the next two years
- Long-term goal: Retire at age 65 with $1 million in savings
- Long-term goal: Travel to Europe during the first year of retirement
Goals play a significant role in shaping your retirement financial planning strategies. They provide a clear target to work towards and help you prioritize where to allocate your resources. For example, if your goal is to retire at age 60 with a certain level of income, you may need to adjust your savings rate or investment strategy to meet that goal. By aligning your financial plan with your retirement goals, you can stay motivated and focused on building a secure financial future.
Understanding Retirement Income Sources
When planning for retirement, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the different sources of income that will support you during your golden years.
Identifying Potential Sources of Retirement Income
- Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans: Such as 401(k) or 403(b) accounts where you contribute a portion of your paycheck towards retirement.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): Traditional IRAs or Roth IRAs that you can contribute to on your own.
- Social Security: A government program that provides a monthly income to retirees based on their work history and contributions.
- Pensions: Some employers offer pensions that provide a fixed monthly income during retirement.
The Role of Social Security in Retirement Planning
Social Security plays a significant role in retirement planning as it provides a reliable source of income for retirees. It is important to understand how much you can expect to receive from Social Security and factor it into your overall financial plan.
The Importance of Diversifying Income Sources for Retirement
Diversifying your sources of retirement income is crucial to ensure financial stability in retirement. Relying on one source of income, such as Social Security, may not be enough to cover all your expenses. By diversifying your income sources, you can better protect yourself against unexpected financial challenges and ensure a comfortable retirement.
Investment Strategies for Retirement
When planning for retirement, it is crucial to consider various investment strategies that can help you build a secure financial future. Different investment options come with varying levels of risk and potential returns, so understanding your goals and risk tolerance is essential.
Comparison of Investment Options
- Stocks: Investing in individual stocks can offer high returns but also comes with high risk due to market fluctuations.
- Bonds: Bonds are considered safer than stocks and provide a steady income stream, making them a more conservative investment option.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio, reducing risk compared to individual stocks.
- Real Estate: Investing in real estate can provide both rental income and potential appreciation of property value over time.
Risk Tolerance and Retirement Investments
- Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial in determining the right investment mix for your retirement portfolio.
- Investors with a higher risk tolerance may opt for more aggressive investments like stocks, aiming for higher returns.
- Conversely, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer safer options like bonds or annuities to protect their principal.
- It’s important to strike a balance between risk and potential returns based on your comfort level and financial goals.
Examples of Investment Vehicles for Retirement
- 401(k) Plans: Employer-sponsored retirement accounts that allow you to contribute pre-tax income and potentially receive matching contributions from your employer.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): Personal retirement accounts that offer tax advantages and a wide range of investment options.
- Annuities: Insurance products that provide a guaranteed income stream for a specified period, offering stability in retirement income.
- Target-Date Funds: Mutual funds designed to automatically adjust asset allocation based on your retirement date, gradually becoming more conservative as you near retirement.
Budgeting and Expense Management in Retirement
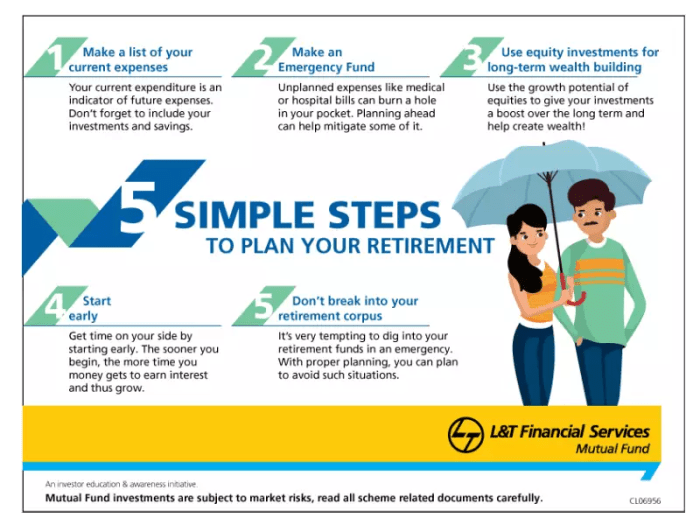
Budgeting and managing expenses during retirement are crucial to ensure financial stability and security. As retirees transition from relying on a steady income to living off savings and investments, having a well-planned budget becomes essential. It helps retirees track their spending, avoid overspending, and make necessary adjustments to maintain their desired lifestyle throughout retirement.
Creating a Retirement Budget
Creating a retirement budget involves outlining all sources of income, including pensions, Social Security benefits, and investment returns, and estimating expenses such as housing, healthcare, transportation, and leisure activities. Here are some tips to help you create a retirement budget:
- Calculate your monthly income and expenses to determine your financial standing.
- Differentiate between essential and discretionary expenses to prioritize your spending.
- Plan for unexpected expenses by setting aside an emergency fund.
- Review and adjust your budget periodically to accommodate changing needs and circumstances.
Controlling Expenses and Adapting to Lifestyle Changes
During retirement, controlling expenses and adapting to lifestyle changes are key to maintaining financial stability. Here are some strategies to help you manage expenses effectively:
- Downsize your living space or consider relocating to a more affordable area to reduce housing costs.
- Limit discretionary spending on non-essential items to avoid depleting your retirement savings.
- Utilize senior discounts and benefits to save money on everyday expenses such as groceries, transportation, and entertainment.
- Explore part-time work or freelance opportunities to supplement your retirement income and cover additional expenses.
Healthcare and Insurance Considerations for Retirement
As you plan for retirement, it’s crucial to consider healthcare and insurance needs to ensure a secure financial future.
Importance of Healthcare Planning in Retirement
Healthcare costs tend to increase as we age, making it essential to factor in medical expenses when creating a retirement budget. Unexpected health issues can significantly impact your finances, so having a solid healthcare plan in place is crucial for a worry-free retirement.
Different Types of Insurance Needed for Retirement
- Medicare: A federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, providing coverage for hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs.
- Medigap Policies: Supplements to fill the gaps left by Medicare, covering co-payments, deductibles, and other expenses not covered by the original plan.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Covers costs associated with long-term care services such as nursing homes or in-home care, which are not covered by Medicare.
How to Factor Healthcare Costs into Retirement Financial Plans
When creating a retirement financial plan, it’s essential to estimate your healthcare costs based on your current health status, family history, and potential medical needs in the future. Consider factors such as premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket expenses to ensure you have enough savings to cover medical bills without compromising your retirement lifestyle.
