When it comes to navigating the complex world of personal finance, one key metric that holds immense importance is the debt-to-income ratio. This ratio plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s financial health and stability. Let’s dive into the world of calculating debt-to-income ratio and unravel its significance in the realm of financial assessments.
As we delve deeper into understanding the components and calculations involved in this ratio, we’ll discover how it impacts financial decisions and the strategies one can adopt to maintain a healthy ratio.
Understanding Debt-to-Income Ratio
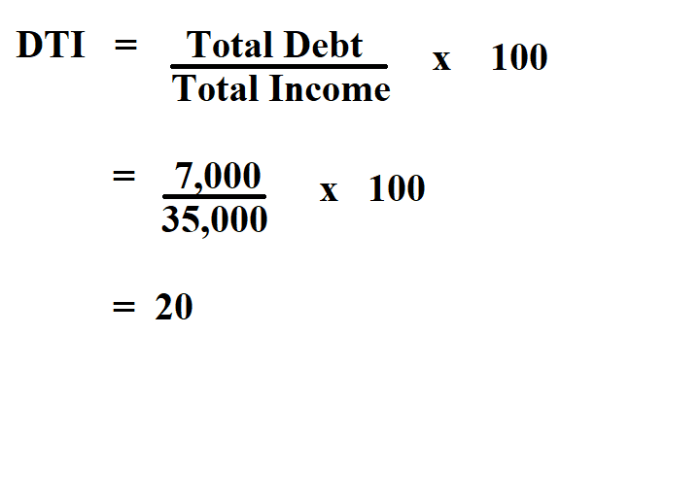
Debt-to-Income Ratio is a financial tool used to assess an individual’s ability to manage their debt payments in relation to their income. It is an important metric for lenders as it helps them determine the borrower’s financial health and likelihood of repayment.
Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio is calculated by dividing the total monthly debt payments by the gross monthly income, and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if someone has total monthly debt payments of $1,500 and a gross monthly income of $5,000, the calculation would be as follows:
Debt-to-Income Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
Debt-to-Income Ratio = ($1,500 / $5,000) x 100 = 30%
Significance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Maintaining a healthy Debt-to-Income Ratio is crucial for financial stability. A lower ratio indicates that a person has manageable debt relative to their income, making them less risky to lenders. This can result in better loan terms, lower interest rates, and easier access to credit. On the other hand, a high Debt-to-Income Ratio may signal financial distress and could lead to difficulty in obtaining new credit or loans.
Components of Debt-to-Income Ratio
When calculating the debt-to-income ratio, it’s important to understand the two main components that make up this financial metric. Debt and income play a crucial role in determining an individual’s financial health and ability to manage their obligations effectively.
Debt
Debt, in the context of the debt-to-income ratio, refers to all the financial obligations that an individual has, including but not limited to:
- Credit card payments
- Car loans
- Student loans
- Mortgage payments
Understanding the total amount of debt a person carries is essential in calculating their debt-to-income ratio accurately.
Income
Income is the other crucial component of the debt-to-income ratio calculation. Income includes all the money that an individual earns, such as:
- Salary or wages
- Bonuses
- Commissions
- Alimony or child support
Knowing the total income a person receives helps determine their capacity to repay their debts and manage their financial responsibilities effectively.
Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
Understanding how to calculate your debt-to-income ratio is crucial in managing your finances effectively. This ratio helps lenders determine your ability to take on more debt responsibly, so it’s essential to know how to calculate it accurately.
Formula for Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
To calculate your debt-to-income ratio, you need to divide your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income. The formula is as follows:
Debt-to-Income Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100%
Step-by-Step Calculation with Real Numbers
Let’s say your total monthly debt payments including your mortgage, car loans, and credit card payments amount to $2,000. If your gross monthly income is $6,000, you can calculate your debt-to-income ratio as follows:
Debt-to-Income Ratio = ($2,000 / $6,000) x 100% = 33.33%
Tips on Interpreting the Calculated Ratio
– A lower debt-to-income ratio (below 20-30%) indicates that you have a manageable level of debt compared to your income.
– A higher ratio (above 30-40%) may suggest that you are carrying too much debt relative to your income and could be at risk of financial strain.
– Lenders typically prefer to see a debt-to-income ratio of 36% or lower when considering loan applications, as it shows that you have sufficient income to cover your debts comfortably.
By understanding and monitoring your debt-to-income ratio, you can make informed decisions about your financial health and take steps to improve it if necessary.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio is a crucial factor that lenders consider when assessing loan eligibility for individuals. It provides insight into a borrower’s ability to manage monthly payments based on their income level.
Why Lenders Use Debt-to-Income Ratio
- Lenders use the debt-to-income ratio to evaluate the risk associated with lending money to an individual.
- A lower debt-to-income ratio indicates that a borrower has more disposable income to cover loan payments, making them a lower risk.
- By using this ratio, lenders can determine whether an individual can comfortably afford additional debt without financial strain.
Impact of High Debt-to-Income Ratio
- A high debt-to-income ratio can limit borrowing opportunities as lenders may view the individual as a higher risk.
- It can lead to higher interest rates on loans, making borrowing more expensive in the long run.
- Having a high debt-to-income ratio can also affect financial decisions such as buying a house or car, as it may impact loan approval and affordability.
Strategies for Improving Debt-to-Income Ratio
- Increasing income through a raise, new job, or side hustle can help lower the debt-to-income ratio.
- Paying off existing debt or consolidating high-interest loans can reduce monthly obligations and improve the ratio.
- Avoid taking on new debt and focus on budgeting and saving to lower the debt-to-income ratio over time.
