When it comes to managing your finances, understanding your debt-to-income ratio is key. This crucial metric helps you evaluate how much of your income goes towards paying off debts, giving you insight into your financial health. Let’s dive into the world of calculating debt-to-income ratio and unravel its importance in the realm of personal finance.
What is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Debt-to-Income Ratio is a financial metric used to measure an individual’s or household’s debt relative to their income. It is a crucial factor in determining one’s financial health and ability to manage debt responsibly.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio is important because it provides insight into how much of a person’s income is being used to repay debts. Lenders use this ratio to assess an individual’s ability to take on additional debt and make timely payments.
Calculation of Debt-to-Income Ratio
To calculate Debt-to-Income Ratio, you need to sum up all monthly debt payments and divide it by gross monthly income. The formula is:
Debt-to-Income Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
Significance of Low or High Debt-to-Income Ratio
- A low Debt-to-Income Ratio (typically below 36%) indicates that an individual has a manageable amount of debt in relation to their income. This is favorable for obtaining new loans and managing finances effectively.
- On the other hand, a high Debt-to-Income Ratio (above 43-50%) suggests that a person may be overleveraged and could struggle to make debt payments. Lenders may view this as a red flag, making it harder to qualify for new credit.
Components of Debt-to-Income Ratio Calculation
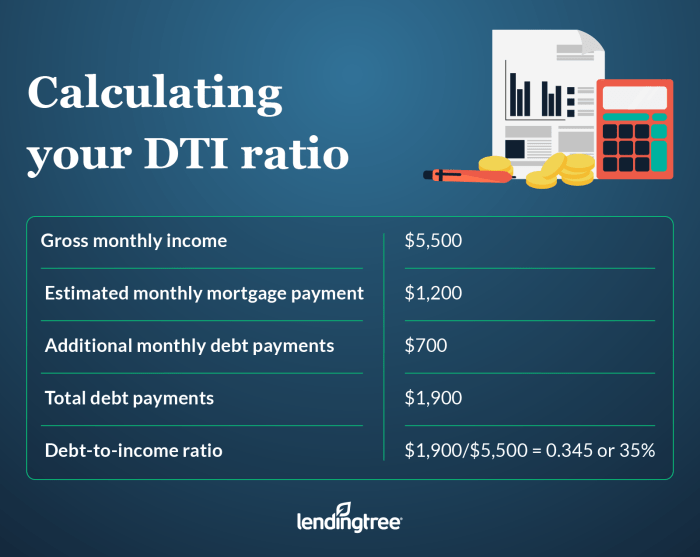
When calculating the Debt-to-Income Ratio, there are specific components that need to be considered. These components include total monthly debt payments and gross monthly income.
Identifying Total Monthly Debt Payments
To determine total monthly debt payments, you need to add up all your monthly debt obligations. This includes payments for credit cards, student loans, car loans, mortgages, and any other debts you may have. Do not include expenses like groceries, utilities, or entertainment.
- Monthly Credit Card Payments: $250
- Student Loan Payment: $300
- Car Loan Payment: $350
- Mortgage Payment: $1,200
Total Monthly Debt Payments = $250 + $300 + $350 + $1,200 = $2,100
Calculating Gross Monthly Income
Gross monthly income refers to the total amount of money you earn before any deductions. This includes your salary, wages, bonuses, alimony, and any other sources of income.
- Salary: $3,500
- Wages: $1,200
- Bonuses: $500
- Alimony: $300
Gross Monthly Income = $3,500 + $1,200 + $500 + $300 = $5,500
Examples of Debt-to-Income Ratio Calculation
Now, let’s calculate the Debt-to-Income Ratio using the components we identified.
Debt-to-Income Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
Debt-to-Income Ratio = ($2,100 / $5,500) x 100 = 38.18%
In this example, the Debt-to-Income Ratio is 38.18%, which means that 38.18% of your gross monthly income goes towards paying off debts. It is important to keep this ratio low to ensure financial stability and better borrowing opportunities.
Interpreting Debt-to-Income Ratio
When it comes to understanding your Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI), it’s crucial to know what the numbers reveal about your financial health. Let’s break down what a low or high DTI signifies and how lenders perceive different ranges.
Low Debt-to-Income Ratio
A low DTI indicates that you have more income available to cover your debts. Lenders view a low DTI favorably as it shows that you are managing your debt responsibly and have a good balance between income and debt obligations.
High Debt-to-Income Ratio
Conversely, a high DTI suggests that a significant portion of your income goes towards paying off debts. This can be a red flag for lenders, signaling potential financial strain and a higher risk of defaulting on payments. A high DTI may limit your ability to take on additional debt or secure favorable loan terms.
Lenders’ Perspective on Different DTI Ranges
Lenders typically categorize DTI ranges as follows:
– DTI below 20%: Excellent – Indicates strong financial health and good debt management.
– DTI between 20% to 35%: Good – Shows a healthy balance between income and debt.
– DTI between 36% to 49%: Fair – Suggests a moderate level of risk for lenders.
– DTI above 50%: Poor – Raises concerns about debt repayment capacity.
Tips to Improve a High Debt-to-Income Ratio
To enhance your DTI and strengthen your financial profile, consider the following tips:
– Increase your income through a raise, bonus, or side hustle.
– Reduce your debt by paying off high-interest balances or consolidating loans.
– Cut down on unnecessary expenses to free up more money for debt payments.
– Avoid taking on new debt to prevent further strain on your DTI ratio.
These strategies can help you lower your DTI over time and improve your financial standing in the eyes of lenders.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio in Financial Decision Making
When it comes to making important financial decisions, understanding your Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI) is crucial. Your DTI is a key factor that lenders consider when evaluating your financial health and creditworthiness. It gives them insight into how much of your income goes towards paying off debt, which helps them determine whether you can handle more debt responsibly.
Impact on Loan Approvals
- Lenders use your DTI to assess your ability to take on more debt. A high DTI may indicate that you are already stretched thin financially, making it less likely for you to get approved for new loans.
- Having a low DTI, on the other hand, shows lenders that you have more room in your budget to take on additional debt, increasing your chances of loan approval.
Creditworthiness Assessment
- Your DTI is a key metric used by lenders to determine your creditworthiness. A high DTI suggests that you may struggle to make timely payments on new debt, which can negatively impact your credit score.
- A low DTI demonstrates to lenders that you are managing your debt responsibly, making you a more attractive borrower with a higher creditworthiness.
Influence on Mortgage Eligibility
- When applying for a mortgage, lenders typically have specific DTI requirements. A lower DTI can increase your chances of qualifying for a mortgage, as it shows that you have a healthier financial profile and are less risky to lend to.
- Conversely, a high DTI may limit your mortgage options or result in higher interest rates, as lenders may view you as a higher risk borrower.
Benefits of a Low Debt-to-Income Ratio
- Having a low DTI not only improves your chances of loan approval and better interest rates but also allows you to save more money for other financial goals, such as building an emergency fund, investing, or saving for retirement.
- A low DTI provides you with more financial flexibility and stability, reducing the stress of living paycheck to paycheck and helping you achieve your long-term financial objectives.
