Diving into the world of Annuities explained, buckle up as we unravel the complexities of this financial tool that plays a crucial role in planning for the future.
From fixed to variable annuities, we’ll explore the ins and outs of each type, shedding light on their benefits and drawbacks.
Annuities Overview
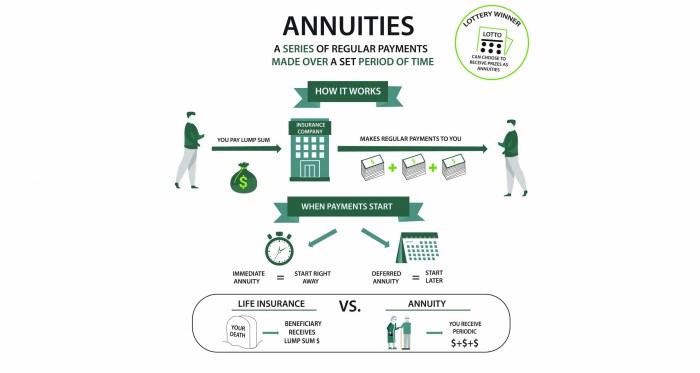
Annuities are financial products designed to provide a steady stream of income during retirement. They work by investing a lump sum or series of payments, which then grow over time and are paid out to the holder either immediately or at a later date.
Types of Annuities
- Fixed Annuities: Guarantee a specific payment amount over a set period.
- Variable Annuities: Allow the holder to invest in different funds, with payouts varying based on market performance.
- Indexed Annuities: Tied to a specific market index, offering the potential for higher returns.
Purposes of Annuities in Financial Planning
Annuities are commonly used to ensure a stable income stream during retirement, protect against outliving savings, and provide tax-deferred growth on investments.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Investing in Annuities
- Benefits:
- Guaranteed income stream for life.
- Tax-deferred growth potential.
- Options for legacy planning.
- Drawbacks:
- High fees and charges.
- Limited liquidity and access to funds.
- Potential for inflation to erode purchasing power.
Types of Annuities
In the world of annuities, there are different types to choose from, each offering unique features and benefits tailored to individual financial goals and preferences.
Fixed Annuities
Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed payout over a specific period of time. The insurance company promises a fixed interest rate, ensuring a steady stream of income for the annuitant. This type of annuity is considered low risk and offers stability in income flow.
Variable Annuities
Variable annuities, on the other hand, offer investment options within the annuity contract. The return on investment is not guaranteed and fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying investments chosen by the annuitant. This type of annuity provides the potential for higher returns but also comes with higher risk.
Indexed Annuities
Indexed annuities are linked to market indexes, such as the S&P 500. They offer the opportunity to earn returns based on the performance of the index, while also providing a level of protection against market downturns. Indexed annuities typically have a minimum guaranteed interest rate, ensuring some level of return even in unfavorable market conditions.
Immediate Annuities vs. Deferred Annuities
Immediate annuities start providing payments shortly after the annuity is purchased, offering an immediate source of income. On the other hand, deferred annuities allow the annuitant to delay payments until a later date, providing the opportunity for the investment to grow before receiving payments. Each type of annuity has its own set of advantages and considerations, depending on the individual’s financial needs and timeline.
Annuity Structures
Annuity structures refer to the different ways in which annuities can be set up to provide payouts and benefits to the annuitant or beneficiaries.
Single and Joint Ownership
Annuities can be structured for single or joint ownership. In single ownership, the annuity is owned by one individual, while joint ownership involves multiple owners, such as spouses. Joint ownership can allow for continued payments to the surviving spouse after the death of the primary annuitant.
Tax Implications
During the accumulation phase, contributions to an annuity are typically made with pre-tax dollars, allowing for tax-deferred growth. However, withdrawals are subject to ordinary income tax and may incur a penalty if taken before a certain age.
Upon distribution, annuity payments are taxed based on the portion of earnings versus principal in each payment. It is important to consult a tax advisor for personalized advice on annuity tax implications.
Additional Features
Annuities often come with additional features that can be added for extra benefits. These may include death benefits that provide a payout to beneficiaries if the annuitant passes away before receiving all payments, as well as riders that offer options for long-term care, inflation protection, or enhanced death benefits. These features can add flexibility and protection to the annuity contract.
Annuity Costs and Fees
When it comes to owning an annuity, there are various fees that you need to be aware of. These fees can impact the overall performance of your annuity and ultimately affect the returns you receive.
Various Fees Associated with Annuities
- Management Fees: These fees are charged by the insurance company to manage your annuity investments. They are typically a percentage of your account value.
- Mortality and Expense (M&E) Fee: This fee covers the insurance risk and expenses associated with the annuity contract.
- Underlying Investment Fees: If your annuity is invested in mutual funds or other investment vehicles, you may incur additional fees related to those investments.
- Rider Fees: If you add optional features or riders to your annuity, such as a guaranteed income rider or a death benefit rider, you may have to pay extra fees.
Surrender Charges and How They Work
Surrender charges are fees you may have to pay if you withdraw money from your annuity before a certain period, typically within the first few years of owning the annuity.
- The surrender period and charges vary depending on the annuity contract, but they are designed to discourage early withdrawals.
- These charges can be a percentage of the amount withdrawn or a flat fee.
Impact of Administrative Fees on Annuity Performance
- Administrative fees cover the costs of maintaining your annuity contract, processing transactions, and providing customer service.
- While administrative fees may seem small, they can add up over time and reduce the overall returns on your annuity.
Cost Structures of Different Types of Annuities
- Fixed Annuities: These annuities typically have lower fees compared to variable annuities, as they offer a guaranteed rate of return.
- Variable Annuities: Variable annuities tend to have higher fees due to the investment options and potential for market exposure.
- Indexed Annuities: Indexed annuities may have a combination of fixed and variable fees, depending on the indexing strategy and features.
